The Future of E-Signatures: AI, Biometrics, and Digital Identity Verification
How Intelligent Identity Systems Are Redefining Trust in the Digital World
E-signatures used to be simple. You opened a document, tapped a box, typed your name, and sent it off. The landscape has since evolved. Cyber threats have become more sophisticated, contracts are more complex, and businesses now expect faster and fully secure digital workflows. This shift has pushed e-signatures far beyond a digital scribble. They now sit at the center of identity verification, fraud prevention, automation, and AI-driven document intelligence.
Intelligent identity systems redefine trust by verifying not only the signature itself but the real identity, intent, and authenticity of every participant involved in the signing process.
As companies accelerate digital transformation, the future of e-signatures focuses on strengthening trust at every stage of the process. That includes trust in who is signing, trust in the integrity of the document, and trust in the security of the workflow from creation to storage. AI, biometrics, and advanced identity verification are the technologies enabling this new era of secure and seamless digital agreements, reshaping how organizations manage identity, maintain compliance, and protect sensitive information.
Key Takeaways:
E-signatures are evolving into identity-first systems, where authentication, fraud prevention, and document intelligence matter more than the signature action itself.
AI enhances security and efficiency by detecting anomalies, reviewing contracts, automating workflows, and predicting bottlenecks across the signing process.
Biometrics and liveness detection add high assurance verification, ensuring the signer is a real, verified individual rather than a spoofed identity or deepfake.
Digital identity wallets and passwordless authentication are becoming standard, enabling fast, reusable, and secure identity verification across platforms and borders.
Regulatory frameworks are moving toward stricter identity requirements, making advanced and qualified electronic signatures essential for industries like finance, healthcare, real estate, and government.
What Modern E-Signatures Really Are Today
E-signatures and digital signatures are often confused, yet they serve different purposes. Traditional e-signatures verify intent. Digital signatures prove authenticity through cryptographic certificates. The systems used today combine both, supported by identity checks, device-level authentication, and audit trails.
These layers matter because businesses are no longer signing simple agreements. They process sensitive financial contracts, healthcare consents, loan documents, government forms, and cross border transactions. As the value and risk increase, so does the need for high assurance identity verification.
The future is moving toward workflows where the signature itself is only one moment in a much larger identity driven security process.
AI: The Intelligence Layer Behind Next Generation E-Signatures
Artificial Intelligence is becoming the brain of future e-signature platforms. It transforms static workflows into dynamic systems that understand context, detect risk, and automate manual work.
AI Fraud Detection and Real Time Threat Monitoring
AI evaluates hundreds of signals during a signing session.
Examples include:
Device fingerprint which identifies the unique hardware and software characteristics of the device being used, making it harder for attackers to hide behind spoofed systems.
IP address and geolocation which confirm whether the signer is in an expected or trusted location, helping detect suspicious access from unusual regions or anonymized networks.
Interaction speed which measures how quickly fields are completed or screens are navigated, revealing automated bots or unnatural signing behavior.
Navigation behavior which analyzes how the signer moves through the document, including scrolling patterns and page dwell times, to identify abnormal or inconsistent activity.
Historical signing patterns which compare current behavior against the signer’s past activity to detect deviations that may indicate impersonation or fraud.
These signals allow platforms to identify unusual behavior instantly. When something appears inconsistent or risky, the system can pause the session, request additional identity proof, or alert the organization. This significantly reduces identity theft, document manipulation, and unauthorized signing.
Intelligent Automation That Removes Manual Work
AI reduces friction by performing tasks that used to slow teams down.
This includes:
Auto filling forms using extracted data which pulls information from uploaded documents, past records, or user profiles to complete fields automatically and minimize manual entry.
Summarizing long contracts for faster review which helps signers and stakeholders understand key terms, obligations, and risks without reading through pages of dense legal text.
Identifying missing fields or inconsistent data which ensures documents are complete, accurate, and compliant before sending them to the next signer, preventing delays and rework.
Routing documents to the correct signers in the right order which organizes complex approval workflows, notifies the right individuals, and keeps the process moving without human coordination.
For businesses handling high volumes of agreements, this level of automation saves time, reduces errors, and creates a smoother, more efficient signing experience for everyone involved.
AI Contract Review and Compliance Scanning
Document intelligence is one of the most valuable applications of AI.
Platforms can identify:
Non standard clauses that deviate from your organization’s usual contract templates, helping teams catch unexpected or unauthorized terms before they become binding.
High risk language such as vague commitments, unclear obligations, or liability shifting wording that could expose the business to legal or financial issues.
Missing regulatory statements required by industry or regional laws, ensuring that contracts meet standards for privacy, consumer protection, data handling, or financial compliance.
Unusual financial terms including inconsistent payment schedules, incorrect amounts, or unexpected fees that may indicate errors or potential fraud.
Inconsistencies in contract versions where older clauses or outdated terms may appear due to copy pasting, manual edits, or mismatched document revisions.
Natural Language Processing helps organizations stay compliant, avoid disputes, and control legal risk long before a signature is added, creating a more reliable and trustworthy contract process.
Predictive Insights for Faster Turnaround
AI can forecast how long a document will take to complete, spot bottlenecks, and recommend changes to speed up negotiations. Over time, this creates smoother approval cycles and more predictable contract timelines.
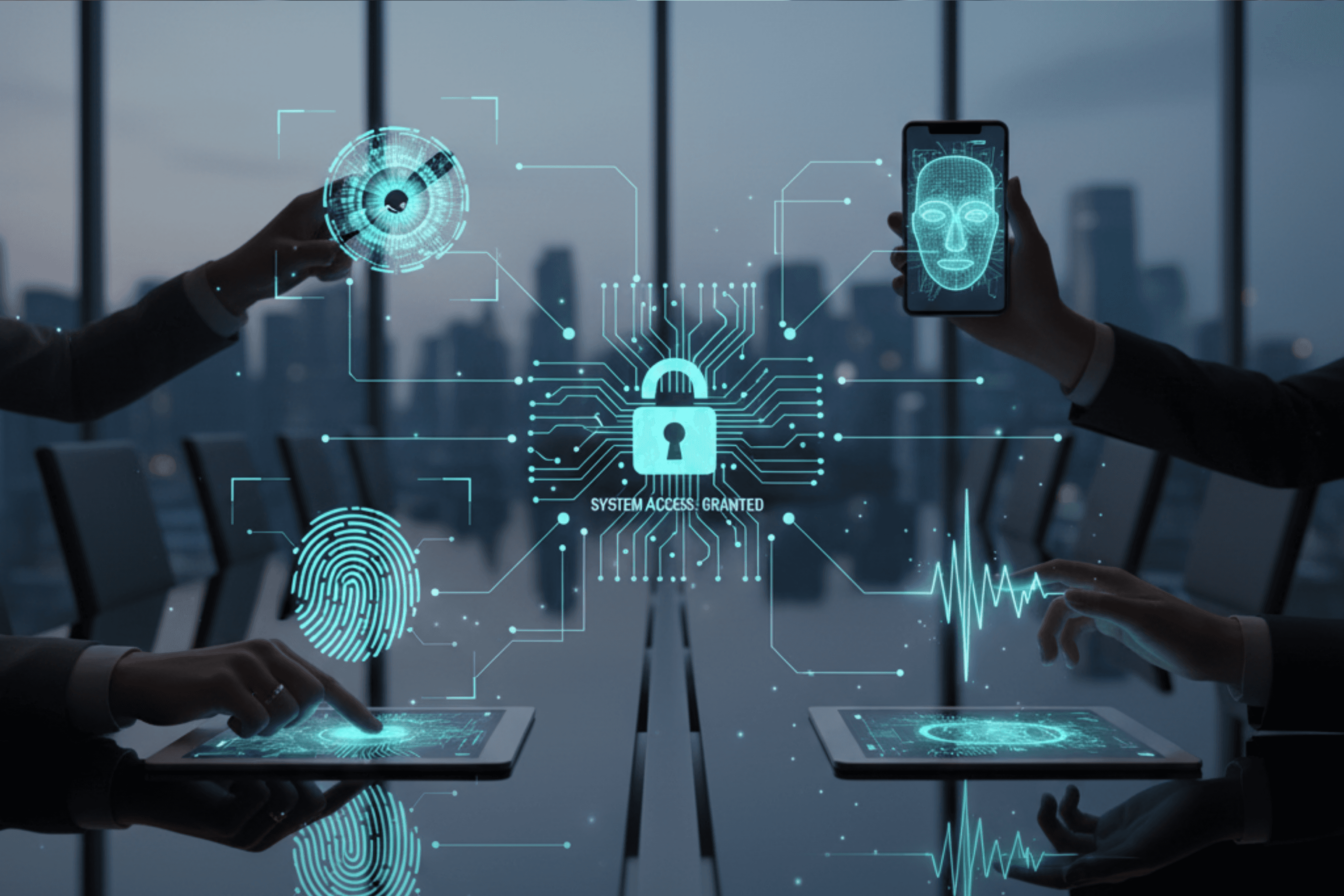
Biometrics: High Assurance Authentication for Digital Signing
Biometric authentication adds a physical or behavioral proof of identity to the signing process. Unlike passwords, biometrics cannot be forgotten, stolen, or forwarded to someone else. This makes them ideal for high-value and regulated transactions.
Biometric Methods Used in E-Signature Workflows
Common biometric verification options include
Facial recognition which maps and analyzes unique facial features to confirm that the person signing matches the verified identity on file.
Fingerprint scanning which uses the distinct patterns of a person’s fingerprint for fast, highly secure authentication on supported devices.
Voice recognition which analyzes vocal tone, rhythm, and speech patterns to verify identity in a hands free and accessible way.
Iris scanning in advanced systems which reads the unique structure of the iris to provide exceptionally accurate and tamper resistant verification.
These methods confirm that the signer is physically present and matches the identity provided, adding a strong layer of trust to digital signing workflows.
Liveness Detection for Anti Spoofing
Deepfakes and AI generated face models are growing risks. Liveness detection solves this by checking for signs of real human presence, such as
Eye movement which evaluates natural blinking patterns and gaze shifts that cannot be replicated by still images or basic video loops.
Depth which measures the three dimensional structure of the face to ensure it is not a flat image or digital rendering.
Texture which analyzes skin detail and surface variation to distinguish a real human face from a screen, printed photo, or synthetic model.
Micro expressions which capture subtle, involuntary facial movements that deepfakes and static masks struggle to reproduce accurately.
Light response which checks how light interacts with the face, ensuring shadows, reflections, and highlights behave naturally.
These techniques prevent attackers from using photos, screens, recordings, or face masks to impersonate someone during a signing session, creating a significantly more secure identity verification process.
Behavioral Biometrics for Continuous Verification
Behavioral data adds another layer of identity confidence.
Examples include
Typing rhythm which analyzes the speed, cadence, and timing of keystrokes to identify patterns that are unique to each individual.
Mouse or touchscreen movement which observes how a person swipes, scrolls, taps, or moves a cursor, revealing distinctive interaction habits.
How a user holds their device which evaluates grip, angle, hand orientation, and movement patterns that remain consistent for each user.
Pressure patterns which track how firmly or lightly someone presses on a touchscreen or keyboard, creating another subtle but unique behavioral marker.
These small details create a unique behavioral signature and verify identity continuously throughout the session, providing ongoing protection rather than a single point of authentication.
The Rise of Digital Identity Verification: A New Foundation of Trust
The Rise of Digital Identity Verification: A New Foundation of Trust
Digital identity verification allows platforms to confirm who someone is using government credentials, biometric checks, and device level authentication. This creates a reusable, verified digital identity that follows the signer across multiple services.
Multi-Factor Identity Checks
Modern verification often combines
Government ID scanning which captures and validates passports, driver’s licenses, or national IDs to confirm the signer’s legal identity.
Live selfie matching which compares a real time photo with the ID document to ensure the person presenting the ID is the same individual.
Biometrics which add a strong, physical proof of identity through facial recognition, fingerprints, or other biometric traits.
Device level authentication which verifies the signer through trusted devices, secure tokens, or passkeys linked to their personal hardware.
Knowledge based checks when needed which may include simple personal questions or account related information to add an additional layer of verification.
This layered approach ensures that the signer is a verified individual, not an assumed or falsified identity, creating a trustworthy and secure signing process.
Digital Identity Wallets and Reusable Credentials
Countries and platforms are introducing digital identity wallets that store verified credentials in one place.
Examples include
Apple Wallet identity cards which allow users to store digital versions of their driver’s licenses or state IDs on their mobile devices for quick, secure verification.
EU Digital Identity Wallet which gives citizens a unified, government backed digital identity that can be used across borders for public services and private sector transactions.
Singapore SingPass which provides residents with a trusted digital identity used for healthcare, banking, government services, and daily digital interactions.
National digital ID systems in many regions which modernize identity management by allowing citizens to access secure digital credentials through official apps or platforms.
With these tools, signers may not need to verify themselves repeatedly. Their authenticated identity will travel securely with them, making digital transactions faster, safer, and far more convenient.
The Move Toward Passwordless Authentication
Passwords create friction and security gaps. E-signature platforms are shifting to
Biometrics which allow users to authenticate using unique physical traits such as facial recognition or fingerprints, offering a fast and secure alternative to passwords.
Passkeys which replace traditional passwords with cryptographic keys stored securely on a device, making login effortless and resistant to phishing or credential theft.
Device bound certificates which link authentication to a trusted device, ensuring only authorized users with that device can access or sign documents.
This shift reduces complexity while increasing trust, creating a smoother and more secure signing experience across digital workflows.
Blockchain and Decentralized Technologies in the Future of E-Signatures
Blockchain introduces tamper-resistant records that improve legal defensibility and long-term trust. These technologies bring transparency, immutability, and decentralization into digital signing workflows, making agreements more secure and verifiable.
Immutable Audit Trails
Every signing action, identity check, timestamp, and device event can be logged on a blockchain ledger. Once stored, these records cannot be altered or deleted, creating a permanent and trustworthy record of the signing process. This strengthens legal proof, supports regulatory compliance, and improves dispute resolution by providing an indisputable history of every action taken.
Smart Contracts That Auto Execute
Smart contracts can trigger actions automatically when certain conditions are met.
Examples include
Releasing payment after signature which ensures funds are sent as soon as all parties sign the agreement.
Updating inventory when a contract triggers supply chain or procurement activities.
Sending automated approval confirmations to streamline workflows and remove the need for manual follow-ups.
These automated processes eliminate delays, reduce administrative overhead, and create faster, error-free digital transactions.
Decentralized Identity (DID)
Decentralized identity gives users full control of their identity credentials. Instead of storing identity data in one central system, credentials are distributed across secure, independent sources. This reduces the risk of large-scale data breaches, enhances privacy, and allows users to present verified identity information without revealing unnecessary personal details. DID ensures that identity verification can be performed securely and consistently across platforms without relying on a single authority.
Security and Compliance in a Changing Regulatory Landscape
Regulators are tightening standards as e-signature technology evolves. Requirements differ across regions, but the overall trend is consistent. Industries are moving toward higher assurance signatures, stronger identity checks, and more detailed audit trails to ensure documents remain valid, secure, and legally defensible across jurisdictions.
Key Frameworks to Understand
ESIGN and UETA in the United States - These laws establish the legal validity of electronic signatures and digital records, setting foundational guidelines for authentication, consent, and record retention.
eIDAS and eIDAS 2.0 in the European Union - The EU framework defines different levels of electronic signatures, including advanced and qualified electronic signatures, which require strict identity verification and secure certificate-based signing.
UK e-signature regulations - After separating from the EU, the UK maintains its own standards aligned with international best practices, ensuring that digital agreements remain legally recognized and compliant.
APAC digital identity and verification requirements - Countries across the Asia Pacific region are adopting modern digital identity systems, government-backed e-signature policies, and strong verification standards to support growing digital economies.
Many sectors such as finance, healthcare, government, and legal services now require advanced or qualified electronic signatures supported by robust identity verification. This ensures that the signer is authenticated, the document is protected from tampering, and the entire workflow meets industry or regulatory expectations.
The Future of Compliance Automation
AI will increasingly
Verify compliance language by identifying whether required legal terms, disclosures, or clauses are present in the document.
Detect missing disclosures to ensure agreements meet industry standards for transparency, privacy, and regulatory obligations.
Generate audit reports that document every action taken throughout the signing process, creating reliable records for legal or regulatory review.
Flag unusual contract behavior such as inconsistent terms, incorrect formatting, unexpected amendments, or suspicious activity during review or signing.
These advancements reduce regulatory risk, help organizations stay compliant, and support consistent policy enforcement across all digital agreements.
Industries That Will Benefit Most from Future Ready E-Signatures
Real Estate and Mortgage Transactions - High-value agreements need strong identity proofing. Biometrics and AI fraud detection lower the risk of impersonation during remote signings and ensure only verified individuals can authorize contracts.
Banking and Fintech - Loan approvals, account openings, investment authorizations, and other financial activities depend on advanced identity verification to prevent fraud and meet strict regulatory standards.
Healthcare - Medical consents, patient authorizations, and insurance documents require accurate identity confirmation and secure audit trails to protect patient safety and maintain compliance.
Legal and HR - Employment documents, contracts, and sensitive agreements rely on high assurance authentication to secure confidential information and reduce unauthorized access.
Government and Public Sector - Citizen services such as tax filings, permits, licenses, and social service applications depend on identity-validated digital workflows for faster, safer, and more reliable online processes.ESIGN and UETA in the United States - These laws establish the legal validity of electronic signatures and digital records, setting foundational guidelines for authentication, consent, and record retention.
How Companies Can Prepare for the Future of E-Signatures
Companies can prepare for the future of e-signatures by first reviewing their current signing workflows to pinpoint security weaknesses, unnecessary steps, and outdated verification methods. Strengthening identity proofing is essential, which includes adopting government ID checks, biometric authentication, and other high-assurance methods that confirm who the signer is with real certainty. Integrating AI into fraud detection and contract review also helps organizations catch risks early, from unusual signing behavior to missing compliance language, reducing the chance of legal or financial exposure.
Beyond technology, preparation requires people and processes to evolve as well. Teams should receive ongoing training to stay updated on compliance requirements and industry specific rules for advanced or qualified electronic signatures. Businesses will also benefit from connecting their e-signature tools with CRM, ERP, and document management systems to create seamless, end to end digital workflows. Keeping a close eye on regulatory developments and upgrading authentication methods as standards evolve ensures the organization remains secure, efficient, and legally aligned as global expectations for digital identity continue to rise.
E-Signatures Are Becoming Identity First and AI-Powered
The next decade of e signatures will not be defined by how people sign. It will be defined by how their identities are verified, how fraud is prevented, and how contracts become smarter and more automated. AI, biometrics, and advanced verification technologies are transforming digital agreements into secure, intelligent, and seamless experiences.
At ROGER, as a Modern Electronic Signature Software, we prioritise reliable verification and smooth automated workflows that make every agreement faster, safer, and easier to manage. Businesses that adopt these capabilities early gain stronger trust, higher efficiency, and reduced compliance risk as fully digital transactions become the global standard.
If you are a startup, small business, or growing team and want a simpler and more secure way to manage agreements, book a call with us to see how ROGER can support your growth.